Treprostinil (Remodulin®)
|
Indications: Treprostinil (Remodulin®) is a prostacyclin vasodilator indicated for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) (WHO Group 1) to diminish symptoms associated with exercise. It is also indicat- ed for patients who require transition from Flolan, to reduce the rate of clinical deterioration.
Mechanism: Treprostinil (Remodulin®) is a prostacyclin analogue. The major pharmacologic actions of tre- prostinil are direct vasodilation of pulmonary and systemic arterial vascular beds and inhibition of platelet aggregation.
Dosing: Continuous subcutaneous infusion (undiluted) is the preferred mode of administration. Use intrave- nous infusion (dilution required) if subcutaneous infusion is not tolerated.
PAH in patients with NYHA Class II-IV symptoms:
- Initial dose for patients new to prostacyclin infusion therapy: 1.25 ng/kg/min (or 0.625 ng/kg/min if not tolerated); dose increase based on clinical response (increments of 1.25 ng/kg/min per week for the first 4weeks of treatment, later 2.5 ng/kg/min per week). Limited experience with doses >40 ng/kg/min. Abrupt cessation of infusion should be avoided.
- Mild to moderate hepatic insufficiency: Initial dose should be decreased to 0.625 ng/kg/min ideal body weight; cautious dosage increase. Not studied in severe hepatic insufficiency.
Subcutaneous Infusion
- Remodulin is administered subcutaneously by continuous infusion, via a self-inserted subcutaneous catheter, using an infusion pump designed for subcutaneous drug delivery. To avoid potential interruptions in drug delivery, the patient must have immediate access to a backup infusion pump and subcutaneous infusion sets.
- For subcutaneous infusion, Remodulin is delivered without further dilution at a calculated Subcutaneous Infusion Rate (mL/hr) based on a patients Dose (ng/kg/min), Weight (kg), and the Vial Strength (mg/mL) of Remodulin being used. During use, a single reservoir (syringe) of undiluted Remodulin can be administered up to 72 hours at 37 degrees (Celsius). The Subcutaneous Infusion rate is calculated using the following formula:
|
|
|

|
|
|
Intravenous Infusion
- Remodulin must be diluted with either Sterile Water for Injection, 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, or Flolan® Sterile Diluent for Injection and is administered intravenously by continuous infusion, via a surgically placed indwelling central venous catheter, using an infusion pump designed for intravenous drug delivery.
- When using an appropriate infusion pump and reservoir, a predetermined intravenous infusionrate should first be selected to allow for a desired infusion period length of up to 48 hours. With this selected Intravenous Infusion Rate (mL/hr) and the patient’s Dose (ng/kg/min) and Weight (kg), the Diluted Intravenous Remodulin Concentration (mg/mL) can be calculated using the following formula:
|
|
|
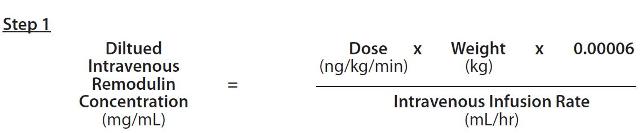
|
|
|
The Amount of Remodulin Injection needed to make the required Diluted Intravenous Remodulin Concentration for the given reservoir size can then be calculated using the following formula:
|
|
|

|
|
|
The calculated amount of Remodulin Injection is then added to the reservoir along with the sufficient vol- ume of diluent to achieve the desired total volume in the reservoir.
Patients Requiring Transition from Flolan
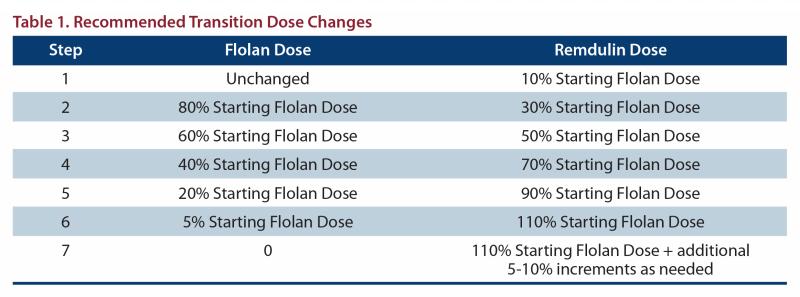
Increase the Remodulin dose gradually as the Flolan dose is decreased, based on constant observation of response. During the transition, Remodulin is initiated at a recommended dose of 10% of the current Flolan dose, and then escalated as the Flolan dose is decreased (see Table 1 for recommended dose titrations).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Efficacy:
Clinical Trials in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH)
Two 12-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind studies compared continuous subcutaneous infusion of Remodulin to placebo in a total of 470 patients with NYHA Class II (11%), III (81%), or IV (7%) pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). The primary endpoint of the studies was change in 6-minute walking distance, a standard measure of exercise capacity. Remodulin was administered as a subcutaneous Infusion as per the package insert dosing instructions, and the dose averaged 9.3 ng/kg/min at Week 12. Few subjects received doses > 40 ng/kg/min.
Hemodynamic Effects:
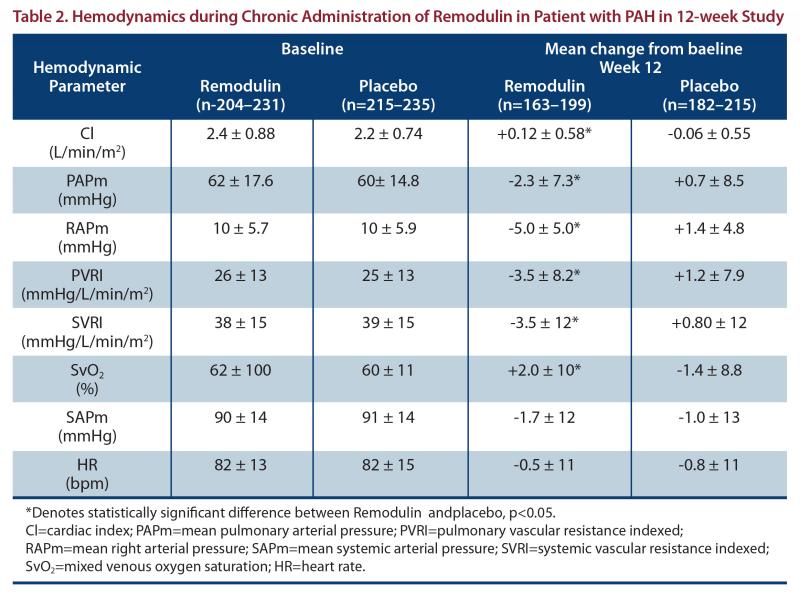
As shown in Table 2, chronic therapy with Remodulin resulted in small hemodynamic changes consistent with pulmonary and systemic vasodilation.
|
|
|
|
|
|
The effect of Remodulin on 6-minute walk, the primary end point of the 12-week studies, was small and did not achieve conventional levels of statistical significance. For the combined populations, the median change from baseline on Remodulin was 10 meters and the median change from baseline on placebo was 0 meters from a baseline of approximately 345 meters. Remodulin also consistently improved indices of dyspnea, fatigue and signs and symptoms of pulmonary hypertension, but these indices were difficult to interpret in the context of incomplete blinding to treatment assignment resulting from infusion site symptoms.
Flolan-To-Remodulin Transition Study
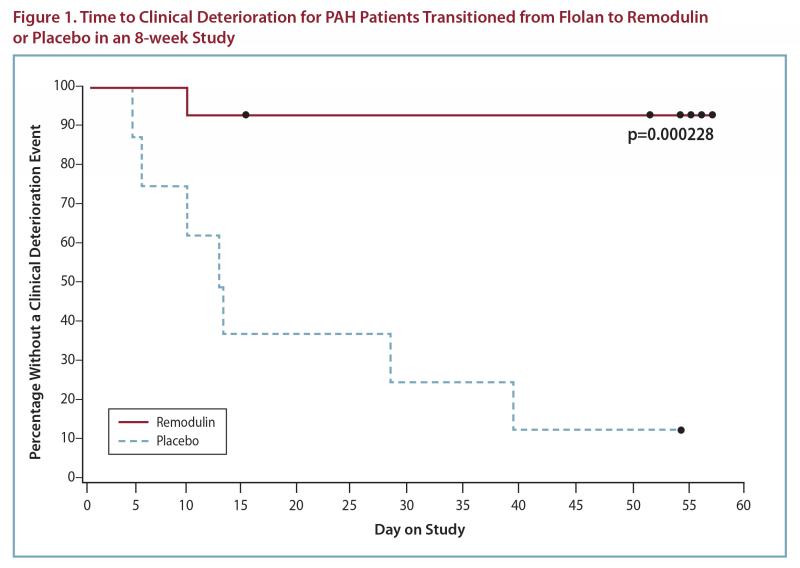
In an 8-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, patients on stable doses of Flolan were randomly withdrawn from Flolan to placebo or Remodulin. Fourteen Remodulin and 8 placebo patients completed the study. The primary endpoint of the study was time to clinical deterioration, defined as either an increase in Flolan dose, hospitalization due to PAH, or death. No patients died during the study.
During the study period, Remodulin effectively prevented clinical deterioration in patients transitioning from Flolan therapy compared to placebo (Figure 1). Thirteen of 14 patients in the Remodulin arm were able to transition from Flolan successfully, compared to only 1 of 8 patients in the placebo arm (p=0.0002).
|
|
|
|
|
|
Adverse Events: Most common adverse events included subcutaneous infusion site pain and reaction, headache, diarrhea, nausea, jaw pain, vasodilatation, dizziness, edema, pruritus and hypotension.
Warnings:
- Chronic intravenous infusions of Remodulin are delivered using an indwelling central venous catheter. This route is associated with the risk of blood stream infections (BSIs) and sepsis, which may be fatal.
- Remodulin should be used only by clinicians experienced in the diagnosis and treatment of PAH.
- Adjust dosage based on clinical response, including infusion site symptoms.
- Do not abruptly lower the dose or withdraw dosing.
- Titrate slowly in patients with hepatic or renal insufficiency, because such patients will likely be exposed to greater systemic concentrations relative to patients with normal hepatic or renal function.
Contraindications: none
Metabolism/Drug interactions: Treprostinil (Remodulin®) is substantially metabolized by the liver, primarily by CYP2C8.
- Blood pressure lowering drugs (e.g., diuretics, antihypertensive agents, or vasodilators): Risk of increased reduction in blood pressure.
- Remodulin inhibits platelet aggregation. Potential for increased risk of bleeding, particularly among patients on anticoagulants.
- Co-administration of a cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2C8 enzyme inhibitor (e.g., gemfibrozil) may increase exposure (both Cmax and AUC) to treprostinil (Remodulin®).
- Co-administration of a CYP2C8 enzyme inducer (e.g., rifampin) may decrease exposure to treprostinil. Increased exposure is likely to increase adverse events associated with treprostinil (Remodulin®) administration, whereas decreased exposure is likely to reduce clinical effectiveness.
Access Program: Product only available through specialty pharmacy with an accompanying Rx and patient enrollment form.
Patient Enrollment form: http://www.remodulin.com/downloads/Franchisereferralforminteractive7-18-2011.pdf
Full US Prescribing Information can be found here: http://www.remodulin.com/downloads/remodulin-prescribinginformation.pdf
|